Abstract
In our diverse world, understanding and embracing neurodiversity cannot be overlooked. Neurodivergence, is a broad term, encompassing a large spectrum of neurological conditions. These conditions challenge the traditional notions of cognitive and behavioral norms of the society. To truly embrace diversity, it becomes crucial to not only acknowledge but actively represent this diverse spectrum in popular media, which is an indispensable instrument for shaping our societal attitudes and culture. This article will take you on a ride into the multilateral landscape of neurodiversity representation in media, acknowledging both progress and shortcomings. It explores the diverse spectrum of neurodivergent identities, and emphasizes the need to move beyond stereotypes.
Neurodivergence and Neurodiversity
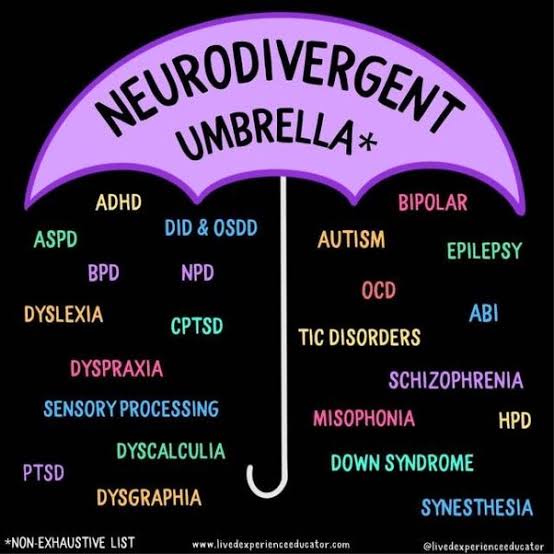
Neurodivergence, refers to the condition where an individual's neurological development and functioning differ from the widely accepted "neurotypical" behaviors or patterns. This umbrella term comprises a wide range of neurological variations, including conditions like autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and others.
Neurodiversity, on the other hand, is the concept that recognizes and acknowledges the diversity of neurological conditions within the human population. It advocates that neurological conditions are natural variations of the human brain, similar to other forms of diversity like ethnicity, gender, or sexual orientation. Neurodiversity promotes acceptance, understanding, and inclusion of all individuals with diverse neurological experiences.
The neurodivergent umbrella encompasses a vast spectrum. Simply put, being a neurodivergent implies that your brain is wired differently than the ‘typical’ configuration. Even left-handed individuals can be categorized as neurodivergent individuals. However, when people commonly refer to neurodivergence, they are usually talking about conditions such as autism, ADHD, dyslexia, dyscalculia, Tourette Syndrome, auditory processing disorder, and other learning-related disorders. Each of these conditions are unique; they come with unique strengths, challenges, and perspectives. By recognizing and celebrating this diversity, we throw away the one-size-fits-all understanding of neurological functioning.
The Importance of Representation in Media
Media, is a reflection of our society, it plays a pivotal role in influencing attitudes and shaping perceptions. When neurodivergent individuals and their experiences are authentically portrayed, it becomes a powerful means to challenge the stereotypes. It bridges the gap between misconceptions and reality. This representation of neurodiversity becomes a lens through which society can see, understand, and ultimately embrace the vast human cognitive diversity.
Positive and accurate portrayals have a profound impact. They not only provide a platform for neurodivergent individuals to see themselves represented but also educate the audience effectively. Authentic representation contributes as myth-busters, they help in scraping down stigmas, and promote empathy. Moreover, they empower neurodivergent individuals by validating their experiences, fostering a sense of belongingness.
Common Neurodivergent Conditions
The ambit of neurodivergent conditions is extensive, reflecting the diversity of human neurological experiences. This consists of a wide range of conditions that impact cognitive, sensory, and social functioning. Individuals who identify as neurodivergent often experience a variety of conditions, including:
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Encompassing conditions like what was previously known as Asperger's syndrome, ASD involves challenges in social communication and behavior, varying widely in severity.
Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): ADHD is characterized by difficulties with attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, impacting various aspects of daily life.
Down Syndrome: Down syndrome results from an extra chromosome and is associated with cognitive delays, distinctive facial features, and certain health challenges.
Dyscalculia: Individuals with dyscalculia experience difficulties with mathematical concepts, making tasks involving numbers challenging.
Dysgraphia: This condition involves challenges with writing, affecting handwriting, spelling, and overall written expression.
Dyslexia: Dyslexia is a learning disorder affecting reading and language processing, leading to difficulties in reading and spelling.
Dyspraxia: Dyspraxia relates to difficulties with coordination and motor skills, impacting tasks like tying shoelaces or using cutlery.
Intellectual Disabilities: Intellectual disabilities involve intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior limitations, affecting everyday social and practical skills.
Mental Health Conditions: Conditions such as Bipolar Disorder, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), and others can co-occur with neurodivergent identities, adding complexity to individuals' experiences.
Prader-Willi Syndrome: A genetic disorder causing a range of physical, mental, and behavioral challenges, including an insatiable appetite.
Sensory Processing Disorders: These disorders affect how the nervous system processes sensory information, leading to challenges in responding to stimuli in the environment.
Social Anxiety: A specific type of anxiety disorder characterized by fear and avoidance of social situations.
Tourette Syndrome: Tourette's involves involuntary movements and vocalizations known as tics, which can vary widely in nature and severity.
Williams Syndrome: A genetic condition characterized by developmental delays, unique facial features, and a friendly and outgoing personality.
Understanding and recognizing this diversity of conditions within the neurodivergent community is vital for providing appropriate support and promoting inclusivity. Each individual's experience is unique, and addressing their specific needs contributes to a more inclusive and compassionate society.
Current Landscape of Neurodivergent Representation in Media
The representation of neurodiversity in the popular media has been a mixed bag, ranging from portrayals that reinforce harmful stereotypes to those that authentically capture the complex challenges of neurodivergent individuals. It is noteworthy that many times there are characters who are not explicitly labeled as neurodivergent, but do exhibit neurodivergent-coded traits. These traits can manifest through their mannerisms and interactions with other characters, subtly indicating neurodivergence.
In recent times, there's been a notable uptick in the inclusion of neurodiverse characters on screen media, and many of these characters received appreciation from the neurodivergent community. For instance, Beth Harmon from Netflix’s widely acclaimed original series, "The Queen's Gambit" is believed to be on the autism spectrum, Beth's singular focus on chess, struggles with social interactions, and her complex relationship with substances contributed to a nuanced and subtle portrayal of autism. The character avoided falling into the common "rude, autistic genius" trope, instead offering a portrayal that highlighted both the triumphs and challenges associated with her neurodivergent traits.
Another example can be found in the popular Netflix series "Stranger Things," where fans have speculated that Eddie Munson, a character known for love for heavy metal and Dungeons and Dragons, is coded as autistic. Some fans even suggest that he may exhibit traits associated with both autism and ADHD. Audiences resonated with Eddie's passion for his special interests and struggles in forming connections and navigating social norms.
Further, the character Sheldon Cooper from the Warner Bros. TV show "The Big Bang Theory" has sparked speculation about whether he exhibits traits associated with autism or Asperger's syndrome. However, it's important to note that the show's creators and writers have not officially confirmed any specific diagnosis for the character. Sheldon is infamous for his highly logical thinking, adherence to routines, social awkwardness, and difficulty to understand social cues, all of which are characteristics that some individuals associate with autism spectrum disorders. The portrayal of Sheldon has prompted discussions about neurodiversity and representation in the media since its first broadcast in 2007.
More notable examples of representations in movies and series are:
Atypical's protagonist, Sam Gardner, who is a high-functioning person with Autism.
Lady Dynamite's Maria, who has OCD and bipolar disorder.
Ozark's character, Tuck, who has Down Syndrome.
The SparkShorts film “Loop†is a short film featuring an authentic non-verbal autistic character. This portrayal is a stride towards a realistic representation of neurodiversity.
Percy Jackson in Percy Jackson and the Lightning Thief, has ADHD and Dyslexia.
Bollywood Movie Taare Zameen Par's (aka Like Stars on Earth) protagonist, Ishaan, suffered from Dyslexia.
These characters have contributed to a growing narrative showcasing more accurate and authentic portrayals of neurodivergent individuals on the screen media. These portrayals not only increased authenticity and depth, but also offered viewers a more nuanced understanding of the diverse experiences of neurodivergent individuals. These portrayals have contributed to a societal shift towards empathy, acceptance, and appreciation for neurodiversity.
But these representations don't fall short of shortcomings; screen media's portrayal of autism has often fallen short of accuracy, frequently reinforcing stereotypes. For example, in shows like "The Good Doctor," the character Dr. Shaun Murphy, is an autistic surgeon, he is pictured as a savant, a characteristic found in only 10 percent of individuals with autism. Moreover, storylines involving autistic characters often miss to mark the challenges neurotypical family members face in accepting their neurodivergent children or siblings. This hinders the authentic representation of life from the perspective of an individual with autism.
While recognizing the diversity within the neurodivergence umbrella, it's vital to note that not every character can encapsulate the experiences of every neurodivergent person, particularly those who are not highly functional.
Similar to the push for representation for POC (people of color) and the LGBTQ+ community, there’s an increase in the number of neurodivergent characters on screen, it has raised awareness and fostered acceptance in recent years. This growing representation contributes to a more refined understanding of neurodivergence. It promotes inclusivity by showcasing the diverse realities of the individuals.
However, a significant concern revolves around stereotyping these identities based on specific traits. It's crucial to acknowledge that no neurodivergent identity is uniform. Our diversity extends as far as our traits do. Whether it's autism, ADHD, dyslexia, or any other neurodivergent identity, each person embodies a unique blend of features and personalities, just like neurotypical individuals. It's essential to understand that not every neurodivergent individual will exhibit the same traits. For instance, not every character depicted as "anti-social but highly intelligent" necessarily represents autism, and not every character displaying "hyperactive and impulsive" behavior signifies ADHD. Each individual's experiences and traits within the neurodivergent spectrum are diverse and multi fold.
The Impact of Authentic Portrayals and Misrepresentation
Authentic portrayals hold a transformative power by influencing societal perceptions and fostering a sense of belonging. When these characters are portrayed with depth and authenticity, the stories become mirrors, reflecting the diverse and complex experiences. Such depictions resonate with individuals who share similar experiences and challenges and serve as windows through which the audience can gain insight into the intricacies of neurodivergence.
Positive representations not only acknowledge the strengths and unique perspectives but also contribute significantly to increased understanding and acceptance. By scraping off stereotypes and fostering compassion these authentic portrayals act as catalysts for breaking down the barriers, promoting inclusivity, and paving the way for a harmonious society.
While there's been a surge in representation in recent years, the portrayal and storytelling is still evolving. More authentic portrayals are needed to capture the complex experiences. It is essential to recognize the progress and advocate for improvements to accurately represent the neurodivergent community.
The ill-consequences of inaccurate representation presses the need for more precise depictions of neurodivergent individuals across all media platforms. Accurate portrayals on screen are vital to providing a clearer understanding of neurodiverse conditions. Every opportunity available to offer insightful representations of various neurological disorders, such as autism, ADHD, and OCD, among others must be seized by the storytellers. Every individual facing neurological challenges deserves recognition for their life-long struggles. Moreover, they deserve the chance to navigate through life, pursue education, employment, or just walk down the street without being subjected to unfair assumptions based on misleading depictions often portrayed on screens. The intersectionality of neurodiversity with other social identities often goes unnoticed. Truthful and respectful portrayals are essential for reshaping societal perceptions and to foster a more inclusive and accepting environment.
A common trope in representing Tourette's sufferers is the "swearing disease," portraying the misconception that all individuals with Tourette’s Syndrome uncontrollably swear and shout obscenities. For instance, Eric Cartman in South Park pretended to have Tourette’s so he could say offensive things; this stereotype is also known as coprolalia, only affects approximately 10 percent of people with the disorder. When the screen media presents these kinds of stereotypes, it transforms a genuine disorder or condition into a punchline or comic relief, drifting away from true representation.
What we truly need is a representation that goes beyond exploiting neurodivergent individuals for entertainment, posing them as laughingstocks. Instead, we should aim for portrayals that capture our everyday lives. A great example of such authentic representation is Netflix’s K-drama Extraordinary Attorney Woo which follows the life of a young autistic attorney, even though it seems yet another savant or genius protagonist, the portrayal effectively captures the challenges of adjusting to adulthood as a person with autism who just wants to fit in, the sense of isolation depicted on screen was something a lot of people could connect to.
The screen media should not overlook the challenges associated with neurodivergence. They should explore other facets of life that intersect with our experiences, such as queer culture, race, socio-economic status, education, work, and relationships with friends and family.
It's important to call out misrepresentation when it occurs. Recognition of problematic portrayals and their elimination will not only foster more accurate representation but will also normalize neurodivergent communities.
Acceptance and Inclusion
Acceptance is a pillar in constructing an inclusive society. When we cultivate an environment that recognizes and celebrates differences and diversity, we lay the foundation for spaces where neurodivergent individuals can not only exist but thrive. This acknowledgment and representation of neurodiversity is not merely about visibility; it is a fundamental step towards acceptance and inclusion.
Representation and awareness plays a pivotal role in achieving this transformative shift. Representation is a powerful tool in challenging the stigmas by providing accurate information and dispelling misconceptions. Moreover, raising awareness is the key to creating a culture of acceptance. It involves bringing neurodivergent experiences into mainstream conversations, enabling our society to move beyond stereotypes and assumptions. By highlighting the strengths, talents, struggles, and unique perspectives of neurodivergent individuals, representation changes societal attitudes.
In accepting and inclusive environments, neurodivergent individuals can feel empowered to express themselves authentically. This empowerment is not only crucial for the well-being of neurodivergent individuals but also for the enrichment of our society. The journey towards acceptance and inclusion is ongoing.
Building a Neurodiverse -Inclusive Future
The path to an inclusive future involves collective efforts. Advocacy is vital in driving positive change. Beyond representation, initiatives promoting neurodiversity in diverse sectors, including education and the workplace, are crucial for creating environments that accommodate and support neurodivergent individuals. Acknowledgment and celebration of the uniqueness of neurodivergent individuals, can lead to genuine appreciation of the diversity.
Embracing neurodiversity through media representation is a crucial step towards the transformative journey to a world where these differences are not only recognized but respected. It is a call to amplify authentic voices, challenge the misconceptions, and contribute towards building a society that values and cherishes the uniqueness of every individual, regardless of their neurological makeup. This creates a foundation for an inclusive future that embraces diversity in its true sense.
By engaging in these collective efforts, we pave the way for a society that not only recognizes neurodiversity but embraces it. A society that is compassionate, empathetic, and provides an equitable future for all.